Google provides a lot of tools for merchants to optimize their SEO and appear higher on search engines. However, if merchants don’t hold enough knowledge about the tools, they can be confused and unsure about their functions and how they can help with their SEO.
Today, in this article, we will explore the differences between the two tools that merchants commonly mistake for : Google Analytics vs Google Tag Manager and how they can help with their SEO.
Before exploring the differences between Google Analytics vs Google Tag Manager, let’s dive into the basic understanding of these two platforms.
What To Know About Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a free web analytics tool provided by Google that helps website owners and marketers understand how users interact with their websites or apps. It collects and organizes data about user behavior, such as how visitors arrive at a site, what pages they view, how long they stay, and whether they complete specific actions like purchases, downloads, or sign-ups.
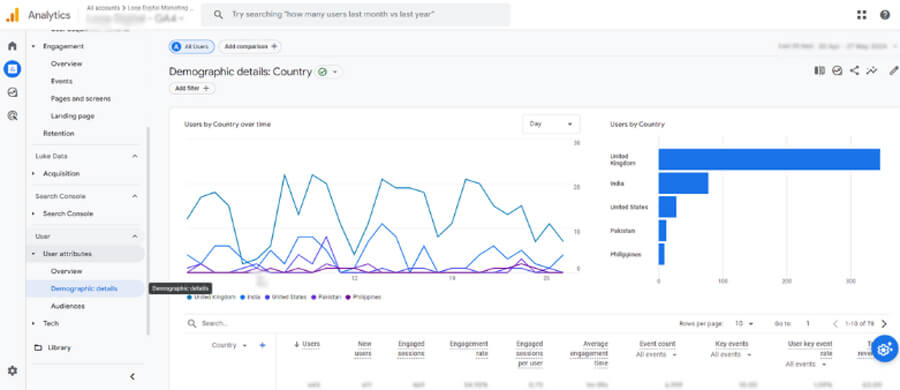
Google Analytics works by placing a small piece of JavaScript tracking code on each page of a website. When someone visits the site, this code sends information back to Google Analytics servers about the user’s session, including details like their device, browser, traffic source (e.g., Google search, social media, or direct visit), and geographic location. The platform then processes this data and presents it in dashboards and customizable reports, making it easy to identify trends, track goals, and measure website effectiveness over time.
Google Analytics also offers advanced features like custom event tracking, conversion funnels, audience segmentation, and integration with other Google tools such as Google Ads and Google Search Console. These capabilities allow users to go beyond basic traffic metrics and analyze deeper aspects of user behavior and marketing performance. Overall, Google Analytics is a powerful tool for anyone looking to grow their online presence by understanding how users engage with their digital content.
What To Know About Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager is a free tag management system created by Google that allows users to manage and deploy tracking codes which are tags, on their websites or mobile applications without having to directly modify the code. The owner can use the tags to send information to third-party tools, such as Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, or other marketing and analytics platforms.
Google Tag Manager works using three main parts: tags, triggers, and variables. Tags are bits of code that track specific actions on your site, like when someone views a page, clicks a button, or submits a form. Triggers control when those tags should activate, such as after a user scrolls through a section or finishes watching a video. Variables help pass extra information, like the product name, device type, or page URL. These parts work together to help you collect detailed user data without adding clutter to your website code.
Once you install the Google Tag Manager code on your website or app, everything else is managed from its online dashboard. You can add, change, or remove tags directly in the platform without editing the site’s code again. This makes it easier for marketers and site owners to control tracking without needing a developer. Google Tag Manager gives you the flexibility to track SEO-related actions and user behavior in a faster, more organized way.
The Differences Between Google Analytics vs Google Tag Manager
With the basic understanding we have got from the previous section, we will now explore the differences between the two platforms: Google Analytics vs Google Tag Manager
- Function:
The function of Google Analytics is to track user interactions and provide detailed reports on website traffic, user behavior, conversions, and more. It helps answer questions like: “How many people visited the site?” or “Which pages are most popular?”
Google Tag Manager, however, does not track data itself. Instead, it functions as a system that decides when and how other tracking tools,like Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, or advertising scripts, should be triggered and run.
- Data Tracking:
Google Analytics is responsible for actually collecting and processing data from your website. It records user sessions, behaviors, goals, and events. Google Tag Manager does not track data by itself. Instead, it sends information to tools like Google Analytics by controlling when those tracking tags are fired based on user actions such as page views, clicks, or scrolls.

- Setup Requirement:
To use Google Analytics, you must add its tracking code to every page you want to track. This often requires modifying your website’s source code, which can be time-consuming.
With Google Tag Manager, you only need to place its container code on your site once. After that, you can manage all your tags and make updates from within the platform without having to change the site code again.
- User Interface:
Google Analytics provides a reporting interface where users can view dashboards, charts, and reports about user behavior and website performance. It is focused on analysis and data visualization.
Google Tag Manager, on the other hand, has a configuration interface where users manage tags, set up triggers, and define variables. It is not used for viewing data, but rather for setting up how and when data is collected.

- Technical Skill Requirements:
Using Google Analytics may require some technical knowledge, especially when setting up custom events, conversion tracking, or working with e-commerce data. Google Tag Manager is often easier for non-developers to use because it allows marketers to implement tracking changes without writing or editing code, though advanced setups may still require some technical input.
How Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager Can Help With Your SEO
If you’re unsure when to use one over the other, knowing the role of Google Analytics vs Google Tag Manager in SEO gives you a clearer picture of how to improve data-driven decisions. By learning how to pair Google Analytics vs Google Tag Manager effectively, you gain better control over both your tracking setup and the resulting insights that fuel SEO strategy.
Google Analytics helps by providing detailed insights into how visitors find and interact with your website through search engines. You can track how much of your traffic comes from organic search, which pages perform best in search results, how long users stay on those pages, and whether they take meaningful actions like signing up or making a purchase. Through the insights you gather from the platform, you will be able to understand what kind of content attracts users and what areas of your site may need improvement. These metrics are crucial for optimizing your content strategy, refining keyword targeting, and ensuring your website aligns with user expectations and search intent.
Google Tag Manager, while not an analytics or reporting tool itself, supports SEO by making it easier to set up and manage tracking for important SEO-related user actions. For example, you can use it to track scroll depth, clicks on internal or outbound links, video engagement, and form submissions without needing to manually edit the website’s code.

This allows marketers and SEO professionals to deploy tags quickly, experiment with tracking elements, and reduce dependency on developers. When combining the data with Google Analytics or other platforms, you will get a fuller picture of how users engage with your content. Google Tag Manager can also be used to add structured data or custom scripts that improve how your content is understood by search engines, which may help boost visibility in search results.
Together, Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager provide the tools to measure SEO performance and track user behavior more accurately, helping you make smarter decisions to improve your site’s search rankings and user experience.
Conclusion
We’ve explored the basics of Google Analytics vs Google Tag Manager, showing how each serves a distinct role. Google Analytics tracks and reports user behavior, while Google Tag Manager manages the tags that send data to tools like Google Analytics.
We also compared how they function, what they track, and how they’re set up. Understanding Google Analytics vs Google Tag Manager is essential for streamlining marketing and improving user data collection.
We have also learned that Google Analytics offers insights into organic traffic and content performance, while Google Tag Manager enables advanced tracking and structured data without needing to change website code.
To boost search rankings, merchants should use these tools effectively alongside others like Google Search Console and Google Ads. Together, they provide a complete view of user behavior and site performance, driving better SEO results.